Adaptive Remeshing (GMSH)#
The RemeshingStrategies can be passed to a GMSH remesher.
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import meshio
import numpy as np
import shapely
from meshwell.cad import cad
from meshwell.mesh import mesh
from meshwell.polysurface import PolySurface
from meshwell.remesh import (
BinaryScalingStrategy,
remesh_gmsh,
)
from meshwell.visualization import plot2D
Define Geometry#
We define two adjacent rectangles with different physical tags.
# Define geometry
large_rect = 10
mid_rect = 2
# Box 1: inner box
polygon1 = shapely.Polygon(
[
[-large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, mid_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, mid_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
],
)
# Box 2: global box
polygon2 = shapely.Polygon(
[
[-large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
],
)
poly_obj1 = PolySurface(
polygons=polygon1,
mesh_order=1,
physical_name="inner_box",
)
poly_obj2 = PolySurface(
polygons=polygon2,
mesh_order=2,
physical_name="outer_box",
)
entities_list = [poly_obj1, poly_obj2]
# Generate CAD
cad(
entities_list=entities_list,
output_file="remesh_example.xao",
)
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : [ 0%] Difference
Info : [ 10%] Difference
Info : [ 20%] Difference - Performing Vertex-Face intersection
Info : [ 30%] Difference
Info : [ 40%] Difference
Info : [ 50%] Difference
Info : [ 60%] Difference
Info : [ 70%] Difference
Info : [ 80%] Difference - Making faces
Info : [ 90%] Difference
Info : [ 0%] Fragments
Info : [ 10%] Fragments
Info : [ 20%] Fragments
Info : [ 30%] Fragments
Info : [ 40%] Fragments
Info : [ 50%] Fragments
Info : [ 60%] Fragments
Info : [ 70%] Fragments
Info : [ 80%] Fragments - Splitting faces
Info : [ 0%] Fragments
Info : [ 10%] Fragments
Info : [ 20%] Fragments
Info : [ 30%] Fragments
Info : [ 40%] Fragments
Info : [ 50%] Fragments
Info : [ 60%] Fragments
Info : [ 70%] Fragments
Info : [ 80%] Fragments - Splitting faces
Info : Writing 'remesh_example.xao'...
Info : Done writing 'remesh_example.xao'
Initial Mesh#
We generate a coarse initial mesh.
# Generate initial mesh
initial_mesh = mesh(
dim=2,
input_file="remesh_example.xao",
output_file="remesh_example_initial.msh",
default_characteristic_length=1.0, # Coarse mesh
n_threads=1,
)
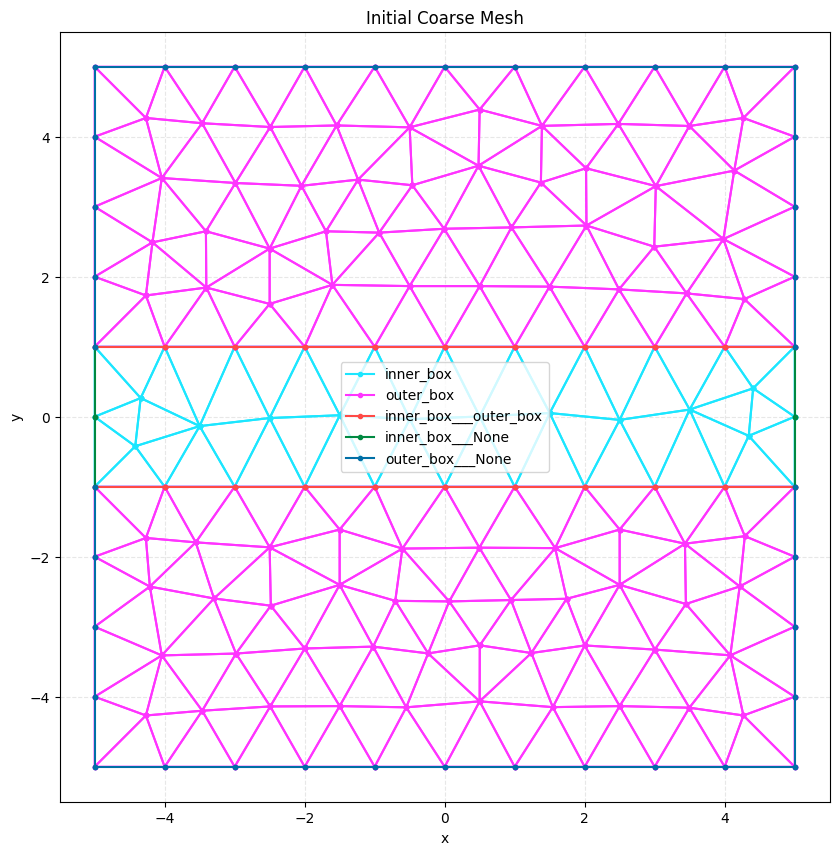
print(f"Initial mesh points: {len(initial_mesh.points)}")
plot2D(initial_mesh, title="Initial Coarse Mesh", wireframe=True)
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'remesh_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example.xao'
Initial mesh points: 151
Define Remeshing Strategy#
We define a strategy that refines the mesh along an oval shape. The strategy function calculates a solution/error (e.g., distance from boundary), and if it exceeds a threshold, refinement is triggered.
# Define oval parameters
center_x, center_y = 0.0, 0.0
radius_x, radius_y = 3.0, 3.0
def oval_looking_data(coords, _data=None):
"""Calculate solution/error based on proximity to oval boundary.
Returns 1.0 if close to boundary, 0.0 otherwise.
"""
x = coords[:, 0]
y = coords[:, 1]
# Normalized distance from center
normalized_dist = ((x - center_x) ** 2 / radius_x**2) + (
(y - center_y) ** 2 / radius_y**2
)
dist_from_boundary = np.abs(np.sqrt(normalized_dist) - 1.0)
# Invert distance: high value near boundary
# e.g., 1.0 at boundary, decaying to 0.0 at distance 1.0
return np.maximum(0, 1.0 - dist_from_boundary)
Visualize Metric Field#
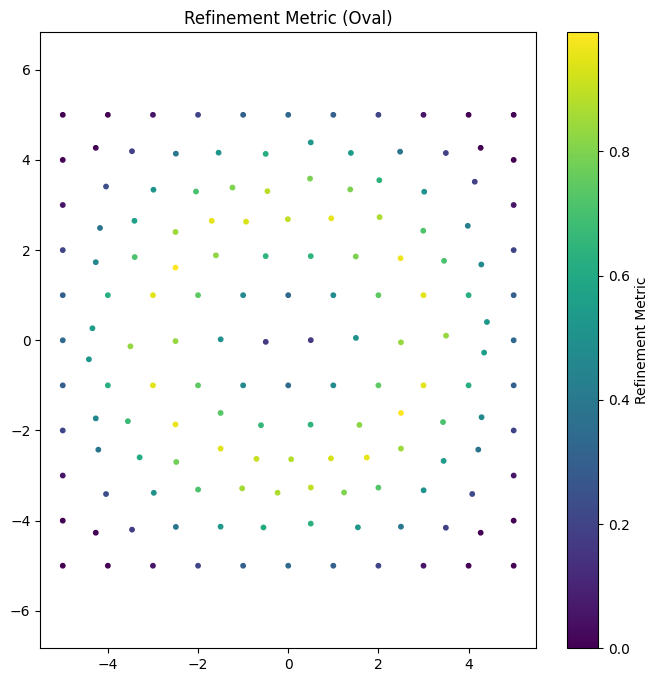
We can visualize the solution/error field on the initial mesh to see where refinement will occur.
# Calculate solution/error on initial mesh points
data_values = oval_looking_data(initial_mesh.points)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.scatter(
initial_mesh.points[:, 0],
initial_mesh.points[:, 1],
c=data_values,
cmap="viridis",
s=10,
)
plt.colorbar(label="Refinement Metric")
plt.title("Refinement Metric (Oval)")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
# refinement_data as (N, 4) -> x, y, z, data
refinement_data = np.column_stack([initial_mesh.points, data_values])
# Create strategy with refinement_data
strategy = BinaryScalingStrategy(
func=oval_looking_data,
threshold=0.7,
factor=0.2,
refinement_data=refinement_data,
min_size=0.1,
max_size=2.0,
field_smoothing_steps=2,
)
size_map = remesh_gmsh(
input_mesh=Path("remesh_example_initial.msh"),
geometry_file=Path("remesh_example.xao"),
output_mesh=Path("remesh_example_final.msh"),
strategies=[strategy],
dim=2,
verbosity=0,
n_threads=1,
)
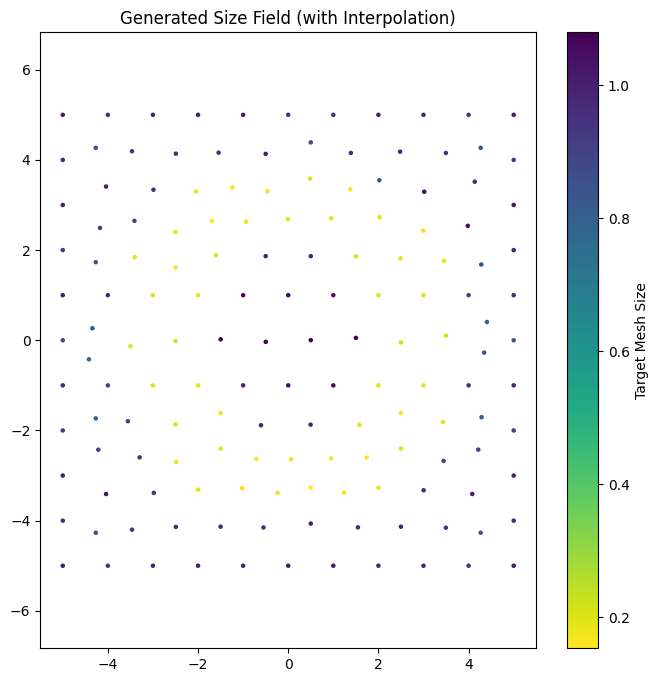
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
# size_map is (N, 4) -> x, y, z, size
sc = plt.scatter(
size_map[:, 0], size_map[:, 1], c=size_map[:, 3], cmap="viridis_r", s=5
)
plt.colorbar(sc, label="Target Mesh Size")
plt.title("Generated Size Field (with Interpolation)")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
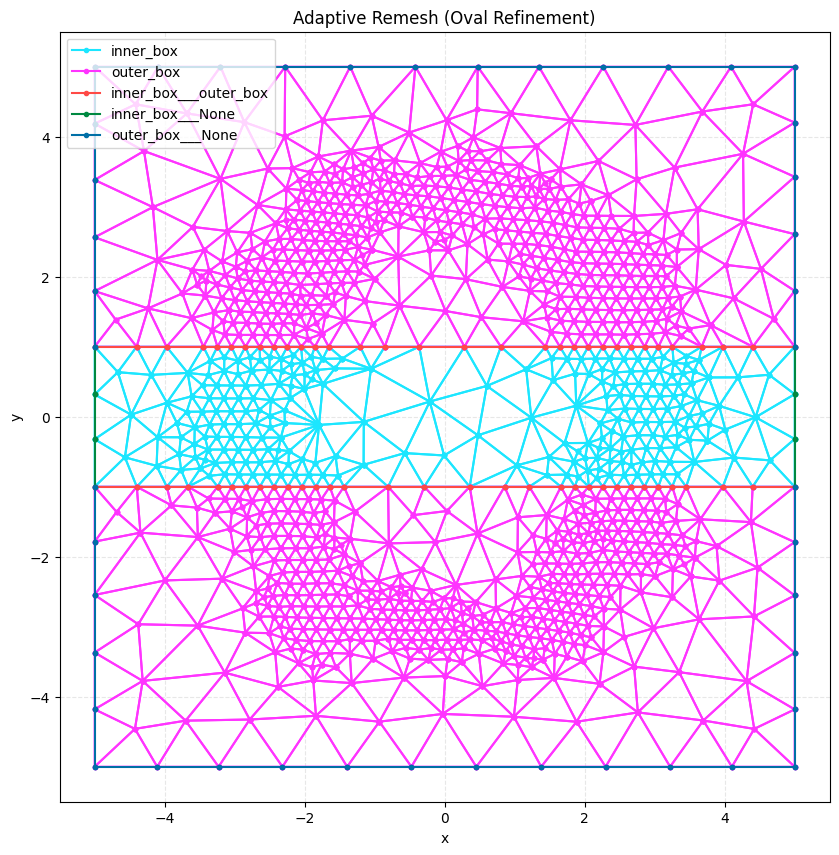
final_mesh = meshio.read("remesh_example_final.msh")
print(f"Final mesh points: {len(final_mesh.points)}")
plot2D(final_mesh, title="Adaptive Remesh (Oval Refinement)", wireframe=True)
Info : Reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'...
Info : 21 entities
Info : 151 nodes
Info : 320 elements
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'remesh_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example.xao'
Final mesh points: 1235
Perform Remeshing with Finer Grid Evaluation#
To capture the oval shape more accurately, we can evaluate the solution/error on a dense grid of points in addition to the mesh nodes. This ensures that features smaller than the initial mesh elements are detected.
# Generate a dense grid of points
x = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 100)
y = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
grid_coords = np.column_stack([X.ravel(), Y.ravel(), np.zeros_like(X.ravel())])
# Evaluate solution/error on the grid
grid_data = oval_looking_data(grid_coords)
# refinement_data as (N, 4) -> x, y, z, data
grid_refinement_data = np.column_stack([grid_coords, grid_data])
# Create strategy with grid refinement data
grid_strategy = BinaryScalingStrategy(
threshold=0.8,
factor=0.2,
refinement_data=grid_refinement_data,
min_size=0.1,
max_size=2.0,
field_smoothing_steps=5,
)
size_map = remesh_gmsh(
input_mesh=Path("remesh_example_initial.msh"),
geometry_file=Path("remesh_example.xao"),
output_mesh=Path("remesh_example_final.msh"),
strategies=[grid_strategy],
dim=2,
verbosity=0,
n_threads=1,
)
Info : Reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'...
Info : 21 entities
Info : 151 nodes
Info : 320 elements
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'remesh_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example.xao'
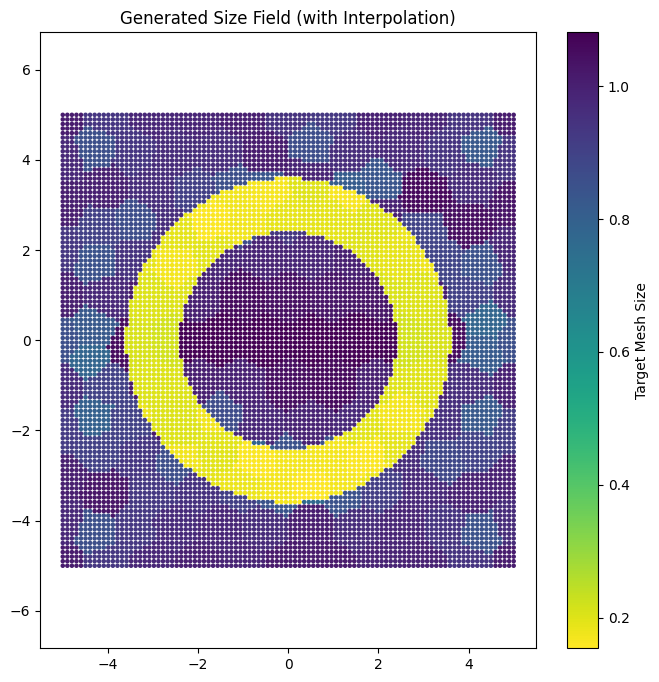
Visualize Size Field#
We can visualize the generated size field, including interpolated points.
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
# size_map is (N, 4) -> x, y, z, size
sc = plt.scatter(
size_map[:, 0], size_map[:, 1], c=size_map[:, 3], cmap="viridis_r", s=5
)
plt.colorbar(sc, label="Target Mesh Size")
plt.title("Generated Size Field (with Interpolation)")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
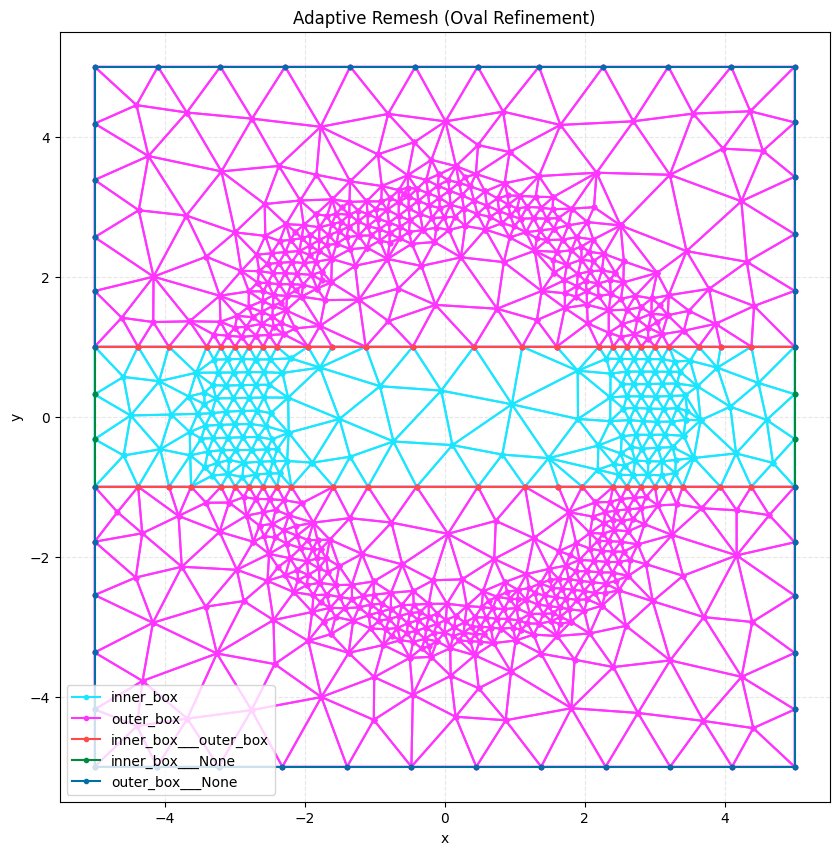
Visualize Result#
We load and plot the final mesh to see the refinement.
final_mesh = meshio.read("remesh_example_final.msh")
print(f"Final mesh points: {len(final_mesh.points)}")
plot2D(final_mesh, title="Adaptive Remesh (Oval Refinement)", wireframe=True)
Final mesh points: 822
Multiple Strategies#
We can combine multiple strategies to refine different regions. Here we’ll refine around a circle and along a vertical line.
# Define circle parameters
circle_center_x, circle_center_y = 2.0, 2.0
circle_radius = 1.5
def circle_looking_data(coords, data=None):
"""Calculate solution/error based on proximity to circle boundary."""
if data is not None:
return data
x = coords[:, 0]
y = coords[:, 1]
# Distance from circle center
dist_from_center = np.sqrt((x - circle_center_x) ** 2 + (y - circle_center_y) ** 2)
dist_from_boundary = np.abs(dist_from_center - circle_radius)
# High value near boundary
return np.maximum(0, 1.0 - dist_from_boundary / 0.5)
# Define line parameters (vertical line at x = -2)
line_x = -2.0
line_width = 0.3
def line_looking_data(coords, data=None):
"""Calculate solution/error based on proximity to vertical line."""
if data is not None:
return data
x = coords[:, 0]
# Distance from line
dist_from_line = np.abs(x - line_x)
# High value near line
return np.maximum(0, 1.0 - dist_from_line / line_width)
# Generate evaluation points for circle
x_circle = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 80)
y_circle = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 80)
X_circle, Y_circle = np.meshgrid(x_circle, y_circle)
circle_coords = np.column_stack(
[X_circle.ravel(), Y_circle.ravel(), np.zeros_like(X_circle.ravel())]
)
circle_data_values = circle_looking_data(circle_coords)
circle_refinement_data = np.column_stack([circle_coords, circle_data_values])
# Generate evaluation points for line
x_line = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 80)
y_line = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 80)
X_line, Y_line = np.meshgrid(x_line, y_line)
line_coords = np.column_stack(
[X_line.ravel(), Y_line.ravel(), np.zeros_like(X_line.ravel())]
)
line_data_values = line_looking_data(line_coords)
line_refinement_data = np.column_stack([line_coords, line_data_values])
# Create strategies
circle_strategy = BinaryScalingStrategy(
func=circle_looking_data,
threshold=0.5, # Lower threshold to refine more area
factor=0.15, # Stronger refinement (smaller factor)
refinement_data=circle_refinement_data,
min_size=0.05, # Much smaller minimum size
max_size=2.0,
field_smoothing_steps=5,
)
line_strategy = BinaryScalingStrategy(
func=line_looking_data,
threshold=0.4, # Lower threshold to refine more area
factor=0.2, # Stronger refinement
refinement_data=line_refinement_data,
min_size=0.08, # Much smaller minimum size
max_size=2.0,
field_smoothing_steps=5,
)
# Combine both strategies
multi_size_map = remesh_gmsh(
input_mesh=Path("remesh_example_initial.msh"),
geometry_file=Path("remesh_example.xao"),
output_mesh=Path("remesh_example_multi.msh"),
strategies=[circle_strategy, line_strategy],
dim=2,
verbosity=0,
n_threads=1,
)
Info : Reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'...
Info : 21 entities
Info : 151 nodes
Info : 320 elements
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example_initial.msh'
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'remesh_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'remesh_example.xao'
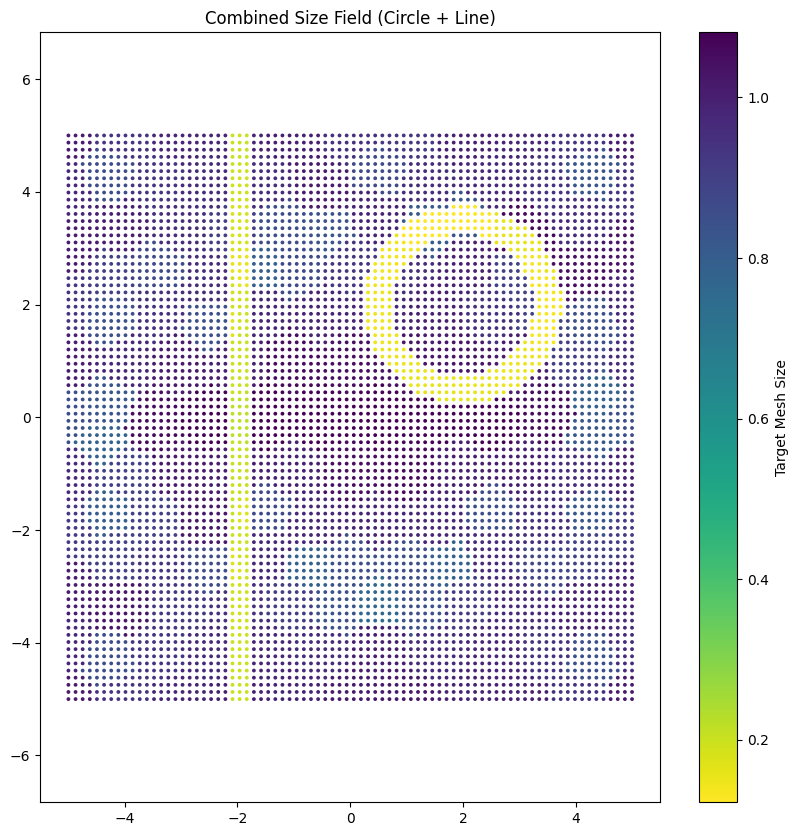
Visualize Multi-Strategy Result#
# Visualize the combined size field
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
sc = plt.scatter(
multi_size_map[:, 0],
multi_size_map[:, 1],
c=multi_size_map[:, 3],
cmap="viridis_r",
s=3,
)
plt.colorbar(sc, label="Target Mesh Size")
plt.title("Combined Size Field (Circle + Line)")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
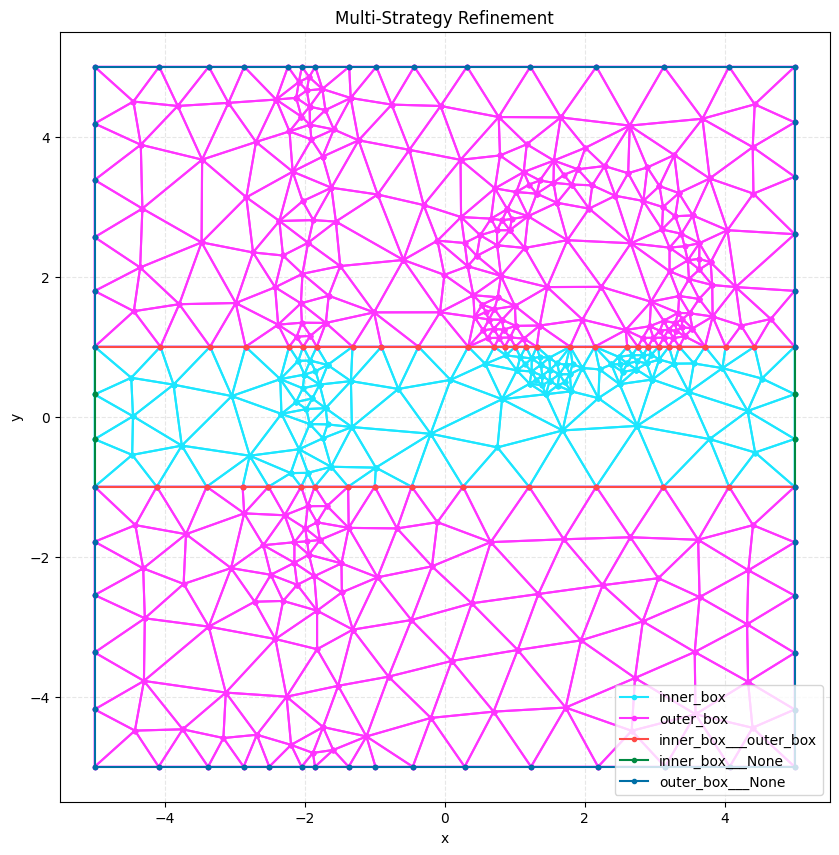
# Load and visualize the final mesh
multi_mesh = meshio.read("remesh_example_multi.msh")
print(f"Multi-strategy mesh points: {len(multi_mesh.points)}")
plot2D(multi_mesh, title="Multi-Strategy Refinement", wireframe=True)
Multi-strategy mesh points: 428
# Clean up files
for f in [
"remesh_example.xao",
"remesh_example_initial.msh",
"remesh_example_final.msh",
"remesh_example_multi.msh",
"remesh_example_3d.xao",
"remesh_example_3d_initial.msh",
"remesh_example_3d_final.msh",
]:
if Path(f).exists():
Path(f).unlink()
Path("remesh_example_direct.msh").unlink(missing_ok=True)