Direct Size Specification#
Meshwell allows you to directly specify the desired mesh size at each point in space using DirectSizeSpecification.
This is useful when you have a pre-calculated size field (e.g., from a physics simulation or an analytical function)
and want to generate a mesh that respects it during the initial meshing process.
Unlike adaptive remeshing, which refines an existing mesh, DirectSizeSpecification is applied during the
generation of the mesh from the CAD geometry.
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import shapely
from meshwell.cad import cad
from meshwell.mesh import mesh
from meshwell.polysurface import PolySurface
from meshwell.resolution import ConstantInField, DirectSizeSpecification
from meshwell.visualization import plot2D
Define Geometry with Multiple Entities#
We’ll define two adjacent rectangles with different physical tags to demonstrate entity-specific application.
# Define geometry
large_rect = 10
mid_rect = 2
# Box 1: inner box
polygon1 = shapely.Polygon(
[
[-large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, mid_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, mid_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, -mid_rect / 2],
],
)
# Box 2: global box
polygon2 = shapely.Polygon(
[
[-large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
[large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2],
[-large_rect / 2, -large_rect / 2],
],
)
poly_obj1 = PolySurface(
polygons=polygon1,
mesh_order=1,
physical_name="inner_box",
)
poly_obj2 = PolySurface(
polygons=polygon2,
mesh_order=2,
physical_name="outer_box",
)
# Generate CAD
cad(
entities_list=[poly_obj1, poly_obj2],
output_file="direct_size_example.xao",
)
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : [ 0%] Difference
Info : [ 10%] Difference
Info : [ 20%] Difference - Performing Vertex-Face intersection
Info : [ 30%] Difference
Info : [ 40%] Difference
Info : [ 50%] Difference
Info : [ 60%] Difference
Info : [ 70%] Difference
Info : [ 80%] Difference - Making faces
Info : [ 90%] Difference
Info : [ 0%] Fragments
Info : [ 10%] Fragments
Info : [ 20%] Fragments
Info : [ 30%] Fragments
Info : [ 40%] Fragments
Info : [ 50%] Fragments
Info : [ 60%] Fragments
Info : [ 70%] Fragments
Info : [ 80%] Fragments - Splitting faces
Info : [ 0%] Fragments
Info : [ 10%] Fragments
Info : [ 20%] Fragments
Info : [ 30%] Fragments
Info : [ 40%] Fragments
Info : [ 50%] Fragments
Info : [ 60%] Fragments
Info : [ 70%] Fragments
Info : [ 80%] Fragments - Splitting faces
Info : Writing 'direct_size_example.xao'...
Info : Done writing 'direct_size_example.xao'
Define Size Field#
We’ll define a size field that varies radially from the center.
def radial_size_function(coords):
"""Define mesh size as a function of distance from center."""
x = coords[:, 0]
y = coords[:, 1]
# Distance from center
dist_from_center = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
# Size grows linearly with distance: 0.1 at center, 1.0 at distance 5
size = 0.1 + (dist_from_center / 5.0) * 0.9
# Clip to reasonable range
return np.clip(size, 0.05, 1.5)
# Generate evaluation grid
x_direct = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 60)
y_direct = np.linspace(-large_rect / 2, large_rect / 2, 60)
X_direct, Y_direct = np.meshgrid(x_direct, y_direct)
direct_coords = np.column_stack(
[X_direct.ravel(), Y_direct.ravel(), np.zeros_like(X_direct.ravel())]
)
# Evaluate size function
direct_sizes = radial_size_function(direct_coords)
# Create refinement data (N, 4) -> x, y, z, size
direct_refinement_data = np.column_stack([direct_coords, direct_sizes])
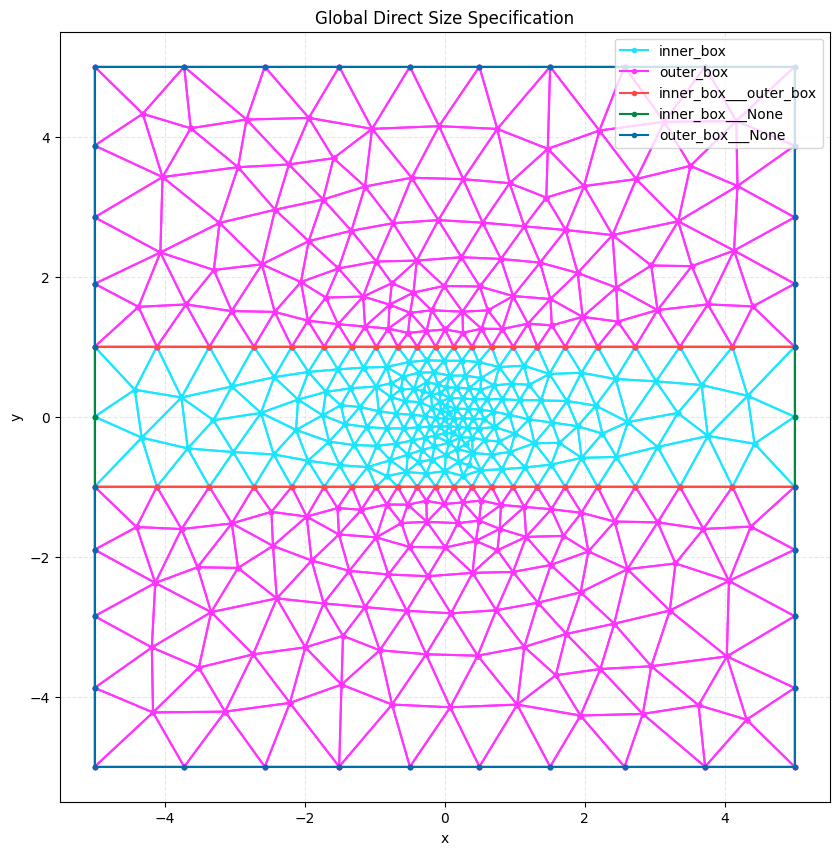
Case 1: Global Application#
We apply the specification globally to the entire model using None as the key.
size_spec_global = DirectSizeSpecification(
refinement_data=direct_refinement_data,
min_size=0.05,
max_size=1.5,
)
mesh_global = mesh(
dim=2,
input_file="direct_size_example.xao",
output_file="direct_size_global.msh",
default_characteristic_length=2.0,
resolution_specs={None: [size_spec_global]}, # Global application
n_threads=1,
)
plot2D(mesh_global, title="Global Direct Size Specification", wireframe=True)
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'direct_size_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'direct_size_example.xao'
Case 2: Combining with Other Resolution Specs#
We can combine DirectSizeSpecification with other specs like ConstantInField.
GMSH will take the minimum size requested by all active fields at any point.
Here, we apply:
The radial size field globally.
A constant fine resolution (0.2) specifically to the “inner_box”.
Inside the inner box, the size will be min(radial_field, 0.2). Since the radial field is ~0.1 at the center
and grows, this will effectively cap the size at 0.2 in the inner box, while allowing it to be smaller near the center.
constant_spec = ConstantInField(
apply_to="surfaces", resolution=0.2 # In 2D, we apply to surfaces
)
mesh_combined = mesh(
dim=2,
input_file="direct_size_example.xao",
output_file="direct_size_combined.msh",
default_characteristic_length=2.0,
resolution_specs={
None: [size_spec_global], # Global radial field
"inner_box": [constant_spec], # Constant fine mesh in inner box
},
n_threads=1,
)
plot2D(
mesh_combined,
title="Combined Specs (Global Radial + Constant Inner)",
wireframe=True,
)
Info : Clearing all models and views...
Info : Done clearing all models and views
Info : Reading 'direct_size_example.xao'...
Info : Done reading 'direct_size_example.xao'

# Clean up files
Path("direct_size_example.xao").unlink(missing_ok=True)
Path("direct_size_global.msh").unlink(missing_ok=True)
Path("direct_size_combined.msh").unlink(missing_ok=True)